Microsoft¶
- Azure AD SAML Enterprise App Auth using Dex
- Azure AD App Registration Auth using OIDC
- Azure AD App Registration Auth using Dex
Azure AD SAML Enterprise App Auth using Dex¶
Configure a new Azure AD Enterprise App¶
- From the
Azure Active Directory>Enterprise applicationsmenu, choose+ New application - Select
Non-gallery application - Enter a
Namefor the application (e.g.Argo CD), then chooseAdd - Once the application is created, open it from the
Enterprise applicationsmenu. - From the
Users and groupsmenu of the app, add any users or groups requiring access to the service.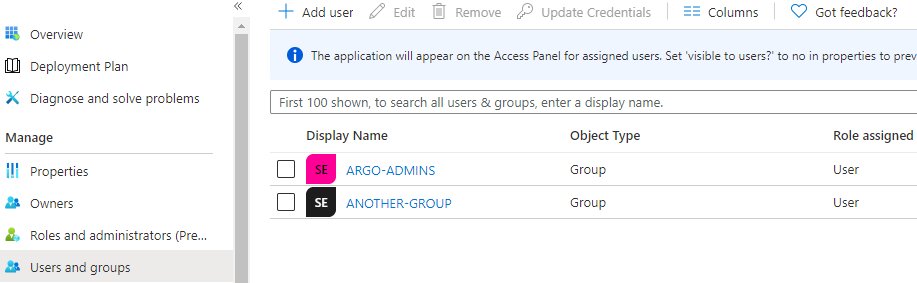
- From the
Single sign-onmenu, edit theBasic SAML Configurationsection as follows (replacingmy-argo-cd-urlwith your Argo URL):- Identifier (Entity ID): https://
<my-argo-cd-url>/api/dex/callback - Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL): https://
<my-argo-cd-url>/api/dex/callback - Sign on URL: https://
<my-argo-cd-url>/auth/login - Relay State:
<empty> - Logout Url:
<empty>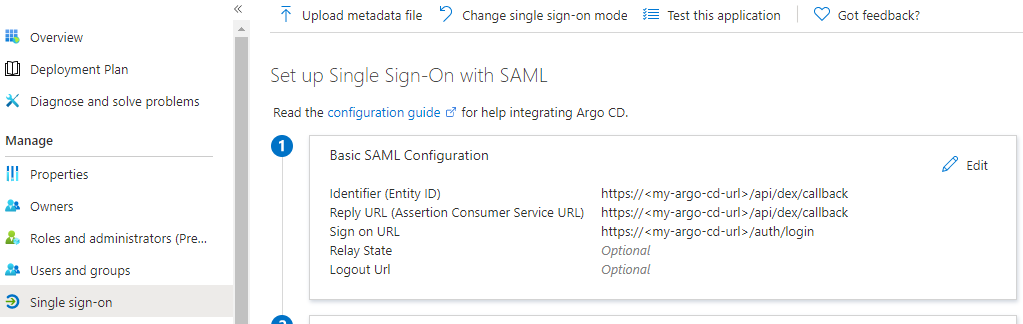
- Identifier (Entity ID): https://
- From the
Single sign-onmenu, edit theUser Attributes & Claimssection to create the following claims:+ Add new claim| Name: email | Source: Attribute | Source attribute: user.mail+ Add group claim| Which groups: All groups | Source attribute: Group ID | Customize: True | Name: Group | Namespace:<empty>| Emit groups as role claims: False- Note: The
Unique User Identifierrequired claim can be left as the defaultuser.userprincipalname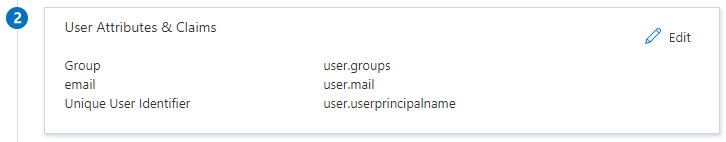
- From the
Single sign-onmenu, download the SAML Signing Certificate (Base64)- Base64 encode the contents of the downloaded certificate file, for example:
$ cat ArgoCD.cer | base64- Keep a copy of the encoded output to be used in the next section.
- From the
Single sign-onmenu, copy theLogin URLparameter, to be used in the next section.
Configure Argo to use the new Azure AD Enterprise App¶
-
Edit
argocd-cmand add the followingdex.configto the data section, replacing thecaData,my-argo-cd-urlandmy-login-urlyour values from the Azure AD App:data: url: https://my-argo-cd-url dex.config: | logger: level: debug format: json connectors: - type: saml id: saml name: saml config: entityIssuer: https://my-argo-cd-url/api/dex/callback ssoURL: https://my-login-url (e.g. https://login.microsoftonline.com/xxxxx/a/saml2) caData: | MY-BASE64-ENCODED-CERTIFICATE-DATA redirectURI: https://my-argo-cd-url/api/dex/callback usernameAttr: email emailAttr: email groupsAttr: Group -
Edit
argocd-rbac-cmto configure permissions, similar to example below.- Use Azure AD
Group IDsfor assigning roles. - See RBAC Configurations for more detailed scenarios.
# example policy policy.default: role:readonly policy.csv: | p, role:org-admin, applications, *, */*, allow p, role:org-admin, clusters, get, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, get, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, create, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, update, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, delete, *, allow g, "84ce98d1-e359-4f3b-85af-985b458de3c6", role:org-admin # (azure group assigned to role)
- Use Azure AD
Azure AD App Registration Auth using OIDC¶
Configure a new Azure AD App registration¶
Add a new Azure AD App registration¶
- From the
Azure Active Directory>App registrationsmenu, choose+ New registration - Enter a
Namefor the application (e.g.Argo CD). - Specify who can use the application (e.g.
Accounts in this organizational directory only). - Enter Redirect URI (optional) as follows (replacing
my-argo-cd-urlwith your Argo URL), then chooseAdd.- Platform:
Web - Redirect URI: https://
<my-argo-cd-url>/auth/callback
- Platform:
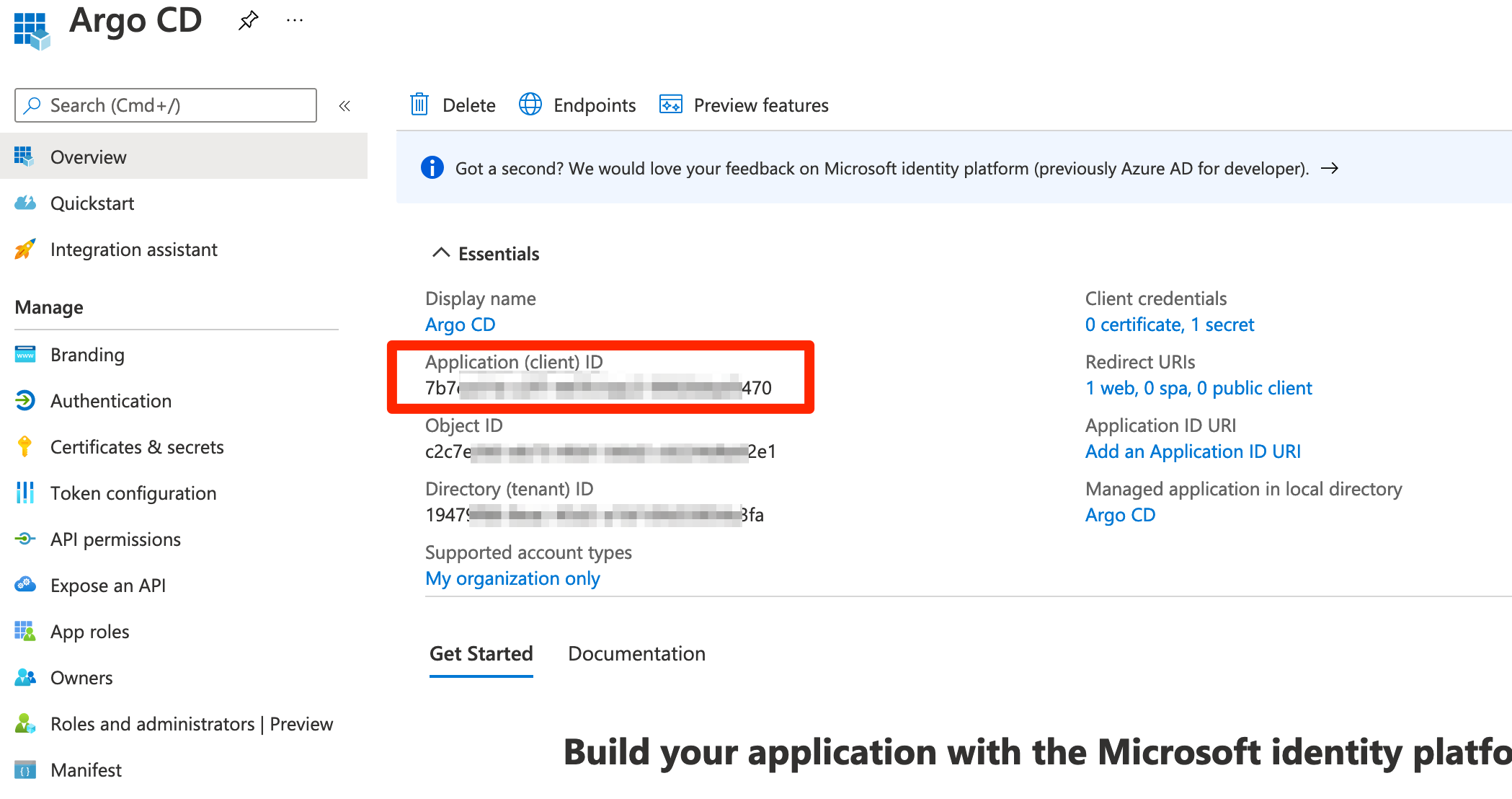
- When registration finishes, the Azure portal displays the app registration's Overview pane. You see the Application (client) ID.
Configure additional platform settings for ArgoCD CLI¶
- In the Azure portal, in App registrations, select your application.
- Under Manage, select Authentication.
- Under Platform configurations, select Add a platform.
- Under Configure platforms, select the "Mobile and desktop applications" tile. Use the below value. You shouldn't change it.
- Redirect URI:
http://localhost:8085/auth/callback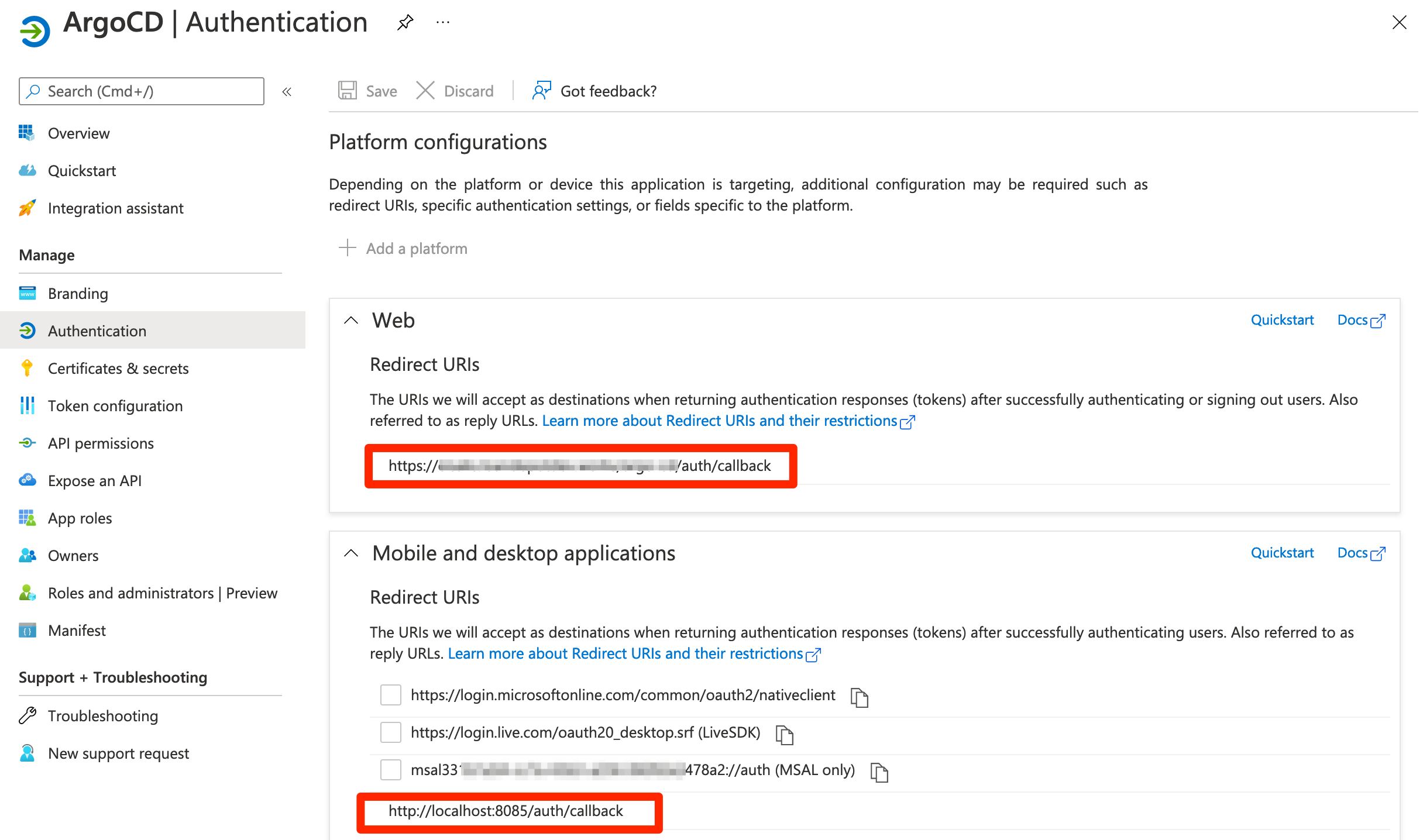
- Redirect URI:
Add credentials a new Azure AD App registration¶
- From the
Certificates & secretsmenu, choose+ New client secret - Enter a
Namefor the secret (e.g.ArgoCD-SSO).- Make sure to copy and save generated value. This is a value for the
client_secret.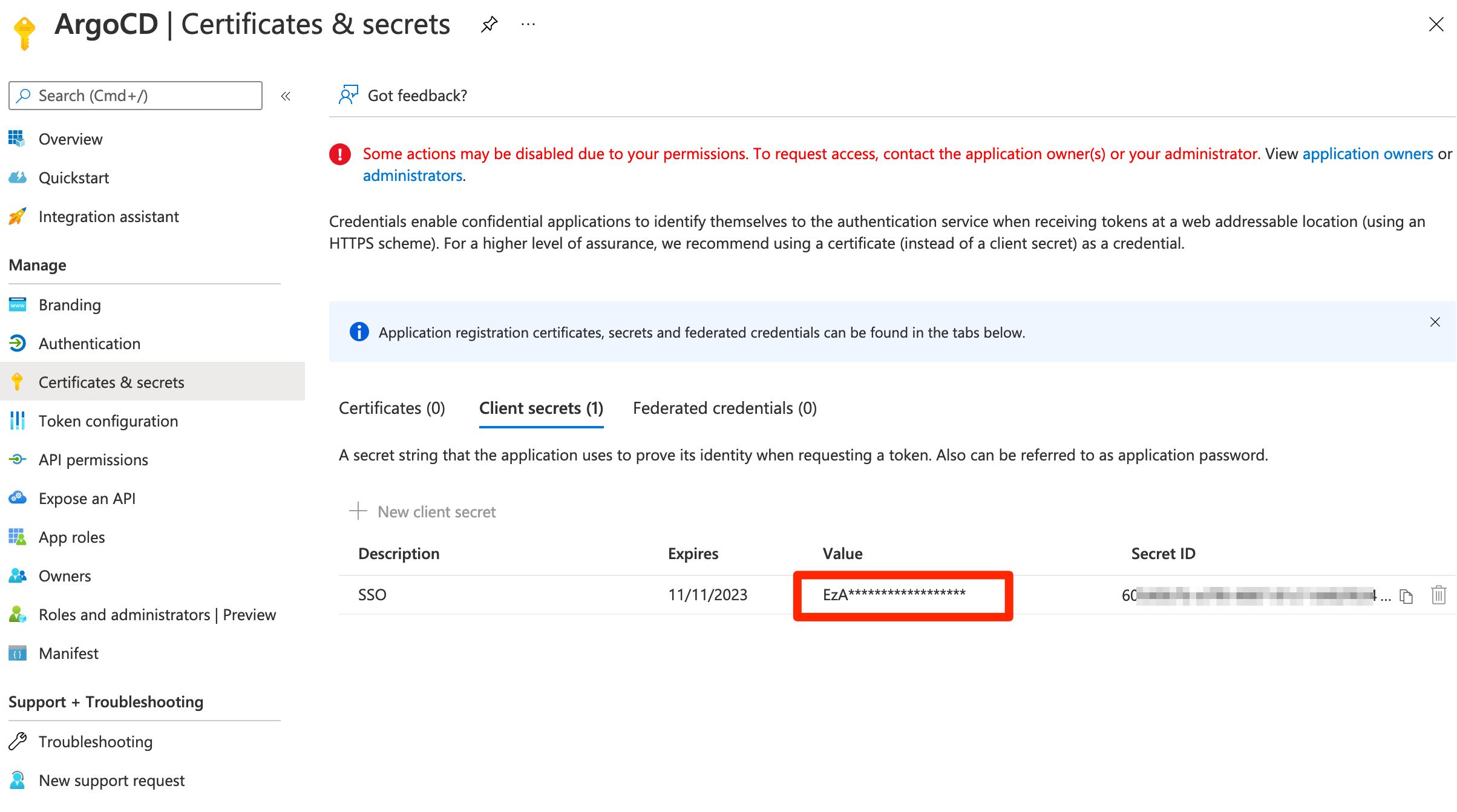
- Make sure to copy and save generated value. This is a value for the
Setup permissions for Azure AD Application¶
- From the
API permissionsmenu, choose+ Add a permission - Find
User.Readpermission (underMicrosoft Graph) and grant it to the created application: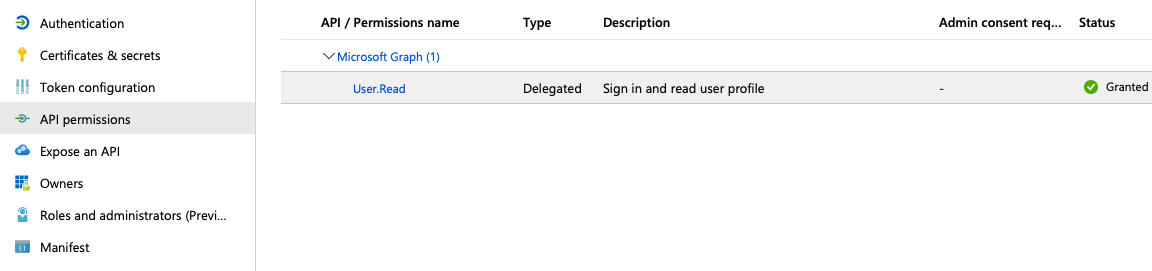
- From the
Token Configurationmenu, choose+ Add groups claim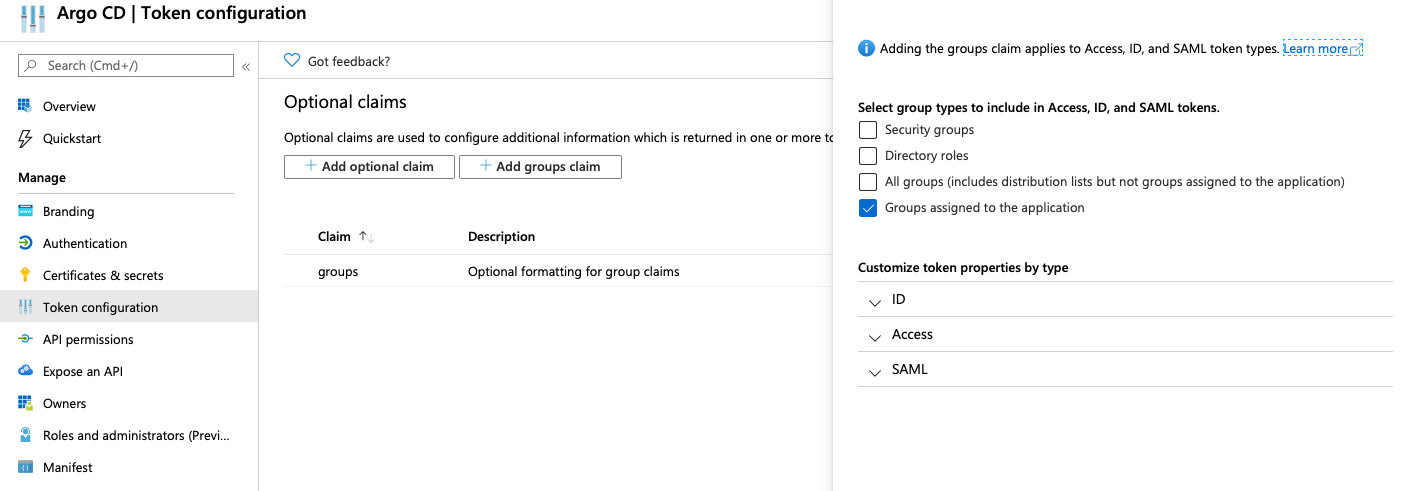
Associate an Azure AD group to your Azure AD App registration¶
- From the
Azure Active Directory>Enterprise applicationsmenu, search the App that you created (e.g.Argo CD).- An Enterprise application with the same name of the Azure AD App registration is created when you add a new Azure AD App registration.
- From the
Users and groupsmenu of the app, add any users or groups requiring access to the service.
Configure Argo to use the new Azure AD App registration¶
-
Edit
argocd-cmand configure thedata.oidc.configsection:ConfigMap -> argocd-cm data: url: https://argocd.example.com/ oidc.config: | name: Azure issuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/{directory_tenant_id}/v2.0 clientID: {azure_ad_application_client_id} clientSecret: $oidc.azure.clientSecret requestedIDTokenClaims: groups: essential: true requestedScopes: - openid - profile - email -
Edit
argocd-secretand configure thedata.oidc.azure.clientSecretsection:Secret -> argocd-secret data: oidc.azure.clientSecret: {client_secret | base64_encoded} -
Edit
argocd-rbac-cmto configure permissions. Use group ID from Azure for assigning roles RBAC ConfigurationsConfigMap -> argocd-rbac-cm policy.default: role:readonly policy.csv: | p, role:org-admin, applications, *, */*, allow p, role:org-admin, clusters, get, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, get, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, create, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, update, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, delete, *, allow g, "84ce98d1-e359-4f3b-85af-985b458de3c6", role:org-admin -
Mapping role from jwt token to argo If you want to map the roles from the jwt token to match the default roles (readonly and admin) then you must change the scope variable in the rbac-configmap.
policy.default: role:readonly policy.csv: | p, role:org-admin, applications, *, */*, allow p, role:org-admin, clusters, get, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, get, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, create, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, update, *, allow p, role:org-admin, repositories, delete, *, allow g, "84ce98d1-e359-4f3b-85af-985b458de3c6", role:org-admin scopes: '[groups, email]'
Refer to operator-manual/argocd-rbac-cm.yaml for all of the available variables.
Azure AD App Registration Auth using Dex¶
Configure a new AD App Registration, as above.
Then, add the dex.config to argocd-cm:
ConfigMap -> argocd-cm
data:
dex.config: |
connectors:
- type: microsoft
id: microsoft
name: Your Company GmbH
config:
clientID: $MICROSOFT_APPLICATION_ID
clientSecret: $MICROSOFT_CLIENT_SECRET
redirectURI: http://localhost:8080/api/dex/callback
tenant: ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff
groups:
- DevOps
Validation¶
Log in to ArgoCD UI using SSO¶
- Open a new browser tab and enter your ArgoCD URI: https://
<my-argo-cd-url>
- Click
LOGIN VIA AZUREbutton to log in with your Azure Active Directory account. You’ll see the ArgoCD applications screen.
- Navigate to User Info and verify Group ID. Groups will have your group’s Object ID that you added in the
Setup permissions for Azure AD Applicationstep.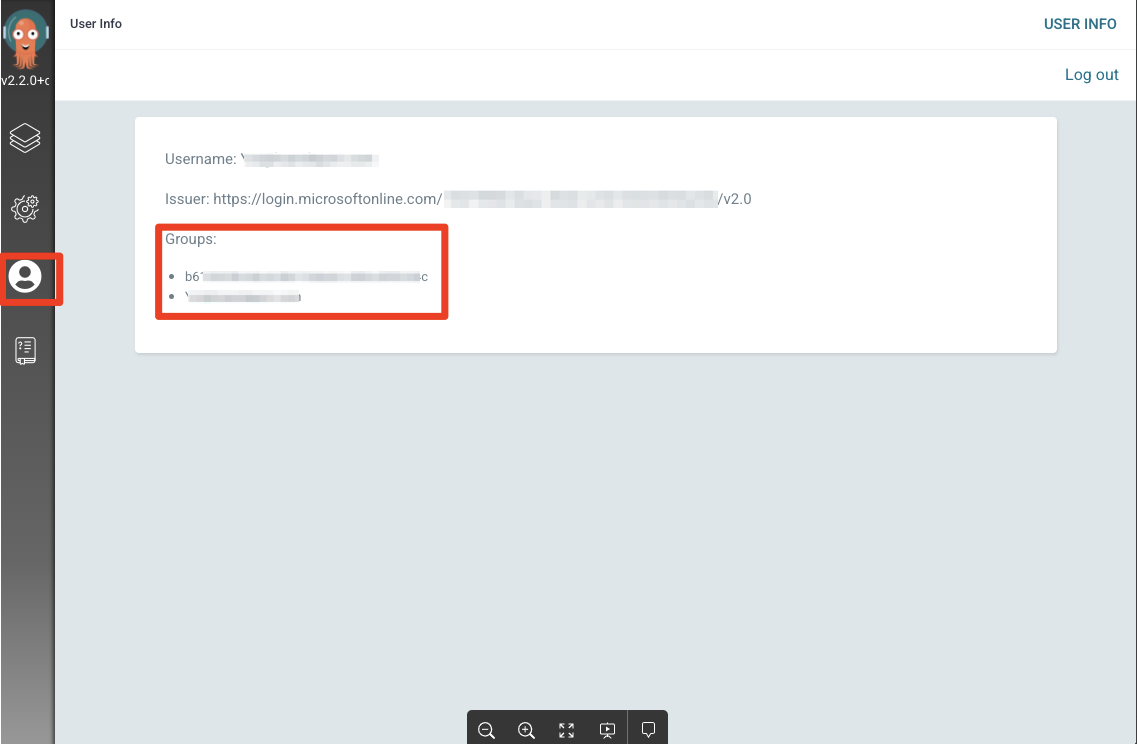
Log in to ArgoCD using CLI¶
-
Open terminal, execute the below command.
argocd login <my-argo-cd-url> --grpc-web-root-path / --sso -
You will see the below message after entering your credentials from the browser.

- Your terminal output will be similar as below.
WARNING: server certificate had error: x509: certificate is valid for ingress.local, not my-argo-cd-url. Proceed insecurely (y/n)? y Opening browser for authentication INFO[0003] RequestedClaims: map[groups:essential:true ] Performing authorization_code flow login: https://login.microsoftonline.com/XXXXXXXXXXXXX/oauth2/v2.0/authorize?access_type=offline&claims=%7B%22id_token%22%3A%7B%22groups%22%3A%7B%22essential%22%3Atrue%7D%7D%7D&client_id=XXXXXXXXXXXXX&code_challenge=XXXXXXXXXXXXX&code_challenge_method=S256&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A8085%2Fauth%2Fcallback&response_type=code&scope=openid+profile+email+offline_access&state=XXXXXXXX Authentication successful 'yourid@example.com' logged in successfully Context 'my-argo-cd-url' updated
You may get an warning if you are not using a correctly signed certs. Refer to Why Am I Getting x509: certificate signed by unknown authority When Using The CLI?.