Parameterized Config Management Plugins¶
Config Management Plugin (CMP) parameterization defines a way for plugins to "announce" and then consume acceptable parameters for an Application. Announcing parameters allows CMPs to provide a UI experience similar to native config management tools (Helm, Kustomize, etc.).
- Parameterized Config Management Plugins
Open Questions¶
- Should we write examples in documentation in Python instead of shell scripts?
It's very easy to write an insecure shell script. People copy/paste code from documentation to start their own work. Maybe by using a different language in examples, we can encourage more secure CMP development.
Summary¶
Config Management Plugins allow Argo CD administrators to define custom manifest generation tooling.
The only existing way for users to parameterize manifest generation is with environment variables.
This proposed feature will allow a plugin to "announce" acceptable parameters for an Application. It will also allow the plugin to consume parameters once the user has set them.
Parameters definitions may be simple (advertising a simple key/value string pair) or more complex (accepting an array of strings or a map of string keys to string values). Parameter definitions can also specify a data type (string, number, or boolean) to help the UI present the most relevant input field.
Motivation¶
1. CMPs are under-utilized¶
CMPs, especially the sidecar type, are under-utilized. Making them more robust will increase adoption. Increased adoption will help us find bugs and then make CMPs more robust. In other words, we need to reach a critical mass of CMP users.
More robust CMPs will make it easier to start supporting tools like Tanka.
2. Decisions about config management tools are limited by the core code¶
For example, there's a Helm bug affecting Argo CD users. The fix would involve importing the Helm SDK (a very large dependency) into Argo CD. Implementing Helm support as a CMP would allow us to use that SDK without embedding it in the core code.
3. Ksonnet is deprecated, and CMPs are a good place to maintain support¶
Offloading Ksonnet to a plugin would allow us to support existing users without maintaining Ksonnet code in the more actively-developed base. But we need CMP parameters to provide Ksonnet support on-par with native support.
Goals¶
Parameterized CMPs must be: * Easy to write * An Argo CD admin should be able to write a simple parameterized CMP in just a few lines of code. * An Argo CD admin should be able to write an advanced parameterized CMP server relying on thorough docs.
Writing a custom CMP server might be preferable if the parameters announcement code gets too complex to be
an inline shell script.
- Easy to install
- Installing a simple CMP or even a CMP with a custom server should be intuitive and painless.
- Easy to use
- Argo CD end-users (for example, developers) should be able to
- View and set parameters in the Argo CD Application UI
- See the parameters reflected in the Application manifest
- Easily read/modify the generated parameters in the manifest (they should be structured in a way that's easy to read)
- CMPs should be able to announce parameters with more helpful interfaces than a simple text field.
- For example, numbers and booleans should be represented in the UI with the appropriate inputs.
- Future-proof
- Since the rich parameters UI is an important feature for config management tools, the parameter definition schema should be flexible enough to announce new types of parameters so the UI can customize its presentation.
- Backwards-compatible
- CMPs written before this enhancement should work fine after this enhancement is released.
- Proven with a rich demonstration
- The initial release of this feature should include a CMP implementation of the Helm config tool. This will
- Serve as a rich example for others CMP developers to mimic
- Allow us to decouple the Helm config management release cycle from the Argo release cycle
- Allow us to work around this bug without including the Helm SDK in the core Argo CD code
- The Helm CMP must be on-par with the native implementation.
- It must present an equivalent parameters UI.
- It must communicate errors back to the repo-server (and then the UI) the same as the native implementation.
Non-Goals¶
We should not: * Re-implement config management tools as CMPs (besides Helm)
Proposal¶
Use cases¶
Use case 1: building Argo CD without config management dependencies¶
As an Argo CD developer, I would like to be able to build Argo CD without including the Helm SDK as a dependency.
The Helm SDK includes the Kubernetes code base. That's a lot of code, and it will make builds unacceptably slow.
Use case 2: writing CMPs with rich UI experiences¶
As an Argo CD user, I would like to be able to parameterize manifests built by a CMP.
For example, if the Argo CD administrator has installed a CMP which applies a last-mile kustomize overlay to a Helm repo, I would like to be able to pass values to the Helm chart without having to manually discover those parameter names (in other words, they should show up in the Application UI just like with a native Helm Application). I also shouldn't have to ask my Argo CD admin to modify the CMP to accommodate the values as environment variables.
Implementation Details/Notes/Constraints¶
Prerequisites¶
Since this proposal is designed to increase CMP adoption, we need to make sure there aren't any bugs that make CMPs less robust than native tools.
Bugs to fix:
1. #8145 - argocd app sync/diff --local doesn't account for sidecar CMPs
2. #8243 - "Configure plugin via sidecar" ⇒ child resources not pruned on deletion
Terms¶
- Parameter announcement: an instance of a data structure which describes an individual parameter that may be applied to a specific Application. (See the schema below.)
- Parameters announcement: a list of parameter announcements. (See the schema below.)
"Parameters" is plural because each "announcement" will be a list of multiple parameter announcements. * Parameterized CMP: a CMP which supports rich parameters (i.e. more than environment variables). A CMP is parameterized if either of these is true: 1. its configuration includes the sections consumed by the default CMP server to generate parameters announcements 2. it is a fully customized CMP server which implements an endpoint to generate parameters announcements
How will the ConfigManagementPlugin spec change?¶
This proposal adds a new parameters key to the ConfigManagementPlugin config spec.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ConfigManagementPlugin
metadata:
name: cmp-plugin
spec:
version: v1.0
generate:
command: ["example.sh"]
discover:
fileName: "./subdir/s*.yaml"
# NEW KEY
parameters:
static:
# The static announcement follows the parameters announcement schema. This is where a parameter description
# should go if it applies to all apps for this CMP.
- name: values-file
title: Values File
tooltip: Path of a Helm values file to apply to the chart.
dynamic:
# The (optional) generated announcement is combined with the declarative announcement (if present). This is where
# a parameter description should be generated if it applies only to a specific app which the CMP handles.
command: ["example-params.sh"]
The currently-configured parameters (if there are any) will be communicated to both generate.command and
parameters.dynamic.command via an ARGOCD_APP_PARAMETERS environment variable. The parameters will be encoded
according to the parameters serialization format defined below.
Passing the parameters to the parameters.dynamic.command will allow configuration of parameter discovery. For example,
if my CMP is designed to handle Kustomize projects which contain Helm charts, I might have the CMP accept an
ignore-helm-charts parameter to avoid announcing parameters for those charts.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
spec:
source:
plugin:
parameters:
- name: ignore-helm-charts
array: [chart-a, chart-b]
How will the CMP know what parameter values are set?¶
Users persist parameter values in an Application's spec.source.plugin.parameters list.
Each parameter has a name and a value stored in the string, array, or map field, according to the parameter's
collectionType. The name should match the name of some parameter announced by the CMP. (But
the user can set any parameter name, so it's the CMP's job to ignore invalid parameters.)
This example is for a hypothetical Helm CMP. This CMP accepts a values and a values-files parameter.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
spec:
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps.git
plugin:
parameters:
- name: values
string: >-
resources:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
- name: values-files
array: [values.yaml]
- name: helm-parameters
map:
image.repository: my.example.com/gcr-proxy/heptio-images/ks-guestbook-demo
image.tag: "0.1"
When Argo CD generates manifests (for example, when the user clicks "Hard Refresh" in the UI), Argo CD will send these
parameters to the CMP as JSON (using the equivalent structure to what's shown above) on an environment variable called
ARGOCD_APP_PARAMETERS.
echo "$ARGOCD_APP_PARAMETERS" | jq
That command, when run by a CMP with the above Application manifest, will print the following:
[
{
"name": "values",
"string": "resources:\n cpu: 100m\n memory: 128Mi"
},
{
"name": "values-files",
"array": ["values.yaml"]
},
{
"name": "helm-parameters",
"map": {
"image.repository": "my.example.com/gcr-proxy/heptio-images/ks-guestbook-demo",
"image.tag": "0.1"
}
}
]
Another way the CMP can access parameters is via environment variables. For example:
echo "$VALUES" > /tmp/values.yaml
helm template --values /tmp/values.yaml .
Environment variable names are set according to these rules:
- If a parameter is a
string, the format isPARAM_{escaped(name)}(escapedis defined below). - If a parameter is an
array, the format isPARAM_{escaped(name_{index})}(where the first index is 0). - If a parameter is a
map, the format isPARAM_{escaped(name_key)}. - If an escaped env var name matches one in the build environment, the build environment variable wins.
- If more than one parameter name produces the same env var name, the env var later in the list wins.
The escaped function will perform the following tasks:
1. It will uppercase the input.
2. It will replace any characters matching this regex with an underscore: [^A-Z0-9_].
The above example will produce the following env vars:
echo "$PARAM_VALUES"
echo "$PARAM_VALUES_FILES_0"
echo "$PARAM_HELM_PARAMETERS_IMAGE_REPOSITORY"
echo "$PARAM_HELM_PARAMETERS_IMAGE_TAG"
The parameters in the Application manifest are represented behind the scenes with the following Go types:
package cmp
// Parameter represents a single parameter name and its value. One of Value, Map, or Array must be set.
type Parameter struct {
// Name is the name identifying a parameter. (required)
Name string `json:"name,omitempty"`
String string `json:"string,omitempty"`
Map map[string]string `json:"map,omitempty"`
Array []string `json:"array,omitempty"`
}
// Parameters is a list of parameters to be sent to a CMP for manifest generation.
type Parameters []Parameter
How will the UI know what parameters may be set?¶
The CMP developer will have two ways to announce acceptable parameters: statically (declaratively) and dynamically.
Static parameter announcements are written directly into the CMP config file:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ConfigManagementPlugin
metadata:
name: helm
spec:
parameters:
static:
- name: values-files
title: Values Files
collectionType: array
Since this hypothetical Helm CMP will accept an array of values.yaml files for every app it handles, the CMP developer can add that parameter as a static parameter announcement in the CMP config.
Dynamic parameters are generated by a CMP developer-defined command.
A parameter definition is an object with following schema:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ConfigManagementPlugin
metadata:
name: helm
spec:
parameters:
dynamic:
command:
- sh
- -c
- |
# Use yq to generate a list of parameters. Then use jq to convert that list of parameters to a parameters
# announcement list.
yq e -o=p values.yaml | jq -nR '
[{
name: "helm-parameters",
title: "Helm Parameters",
tooltip: "Parameters to override when generating manifests with Helm",
collectionType: "map",
map: (inputs | capture("(?<key>.*) = (?<value>.*)") | from_entries)
}]'
For a Helm chart with only an image.repository and image.tag in values.yaml, the parameter announcement would look
like this:
[
{
"name": "helm-parameters",
"collectionType": "map",
"title": "Helm Parameters",
"tooltip": "Parameters to override when generating manifests with Helm",
"map": {
"image.repository": "my.example.com/gcr-proxy/heptio-images/ks-guestbook-demo",
"image.tag": "0.1"
}
}
]
Before sending a parameters announcement to the UI, the CMP server will combine the static and dynamic parameters. (Behind the scenes, the list is actually communicated to the UI via gRPC, but they're presented here as JSON for readability.)
[
{
"name": "values-files",
"title": "Values Files",
"collectionType": "array"
},
{
"name": "helm-parameters",
"collectionType": "map",
"title": "Helm Parameters",
"tooltip": "Parameters to override when generating manifests with Helm",
"map": {
"image.repository": "my.example.com/gcr-proxy/heptio-images/ks-guestbook-demo",
"image.tag": "0.1"
}
}
]
This is the full parameters announcement schema as Go types.
package cmp
// ParameterItemType is the primitive data type of each of the parameter's value (or each of its values, if it's an array or
// a map).
type ParameterItemType string
// Anything besides "number" and "boolean" is treated as string.
const (
ParameterItemTypeNumber ParameterItemType = "number"
ParameterItemTypeBoolean ParameterItemType = "boolean"
)
// ParameterCollectionType is a parameter's value's type - a single value (like a string) or a collection (like an array or a
// map).
type ParameterCollectionType string
// Anything besides "number" and "boolean" is treated as string.
const (
ParameterCollectionTypeMap ParameterCollectionType = "map"
ParameterCollectionTypeArray ParameterCollectionType = "array"
)
// ParameterAnnouncement represents a CMP's announcement of one acceptable parameter (though that parameter may contain
// multiple elements, if the value holds an array or a map).
type ParameterAnnouncement struct {
// Name is the name identifying a parameter. (required)
Name string `json:"name,omitempty"`
// Title is a human-readable text of the parameter name. (optional)
Title string `json:"title,omitempty"`
// Tooltip is a human-readable description of the parameter. (optional)
Tooltip string `json:"tooltip,omitempty"`
// Required defines if this given parameter is mandatory. (optional: default false)
Required bool `json:"required,omitempty"`
// ItemType determines the primitive data type represented by the parameter. Parameters are always encoded as
// strings, but ParameterTypes lets them be interpreted as other primitive types.
ItemType ParameterItemType `json:"itemType,omitempty"`
// CollectionType is the type of value this parameter holds - either a single value (a string) or a collection (array or map).
// If Type is set, only the field with that type will be used. If Type is not set, `string` is the default. If Type
// is set to an invalid value, a validation error is thrown.
CollectionType ParameterCollectionType `json:"collectionType,omitempty"`
String string `json:"string,omitempty"`
Map map[string]string `json:"map,omitempty"`
Array []string `json:"array,omitempty"`
}
// ParametersAnnouncement is a list of announcements. This list represents all the parameters which a CMP is able to
// accept.
type ParametersAnnouncement []ParameterAnnouncement
Implementation Q/A¶
- Question: What do we do if the CMP announcement sets more than one
value.{collection}?
Answer: We ignore all but the configured collectionType.
- name: images
collectionType: map
array: # this gets ignored because collectionType is 'map'
- ubuntu:latest=docker.example.com/proxy/ubuntu:latest
- guestbook:v0.1=docker.example.com/proxy/guestbook:v0.1
map:
ubuntu:latest: docker.example.com/proxy/ubuntu:latest
guestbook:v0.1: docker.example.com/proxy/guestbook:v0.1
- Question: What do we do if the CMP user sets more than one of
value/array/mapin the Application spec?
Answer: We send all given information to the CMP and allow it to select the relevant field.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
spec:
source:
plugin:
parameters:
- name: images
array: # this gets sent to the CMP, but the CMP should ignore it
- ubuntu:latest=docker.example.com/proxy/ubuntu:latest
- guestbook:v0.1=docker.example.com/proxy/guestbook:v0.1
map:
ubuntu:latest: docker.example.com/proxy/ubuntu:latest
guestbook:v0.1: docker.example.com/proxy/guestbook:v0.1
- Question: How will the UI know that adding more items to an array or a map is allowed?
Answer: Always assume it's allowed to add to a map or array.
- name: images
collectionType: map # users will be allowed to add new items, because this is a map
map:
ubuntu:latest: docker.example.com/proxy/ubuntu:latest
guestbook:v0.1: docker.example.com/proxy/guestbook:v0.1
If the CMP author wants an immutable array or map, they should just break it into individual parameters.
- name: ubuntu:latest
string: docker.example.com/proxy/ubuntu:latest
- name: guestbook:v0.1
string: docker.example.com/proxy/guestbook:v0.1
- Question: What do we do if a CMP announcement doesn't include a
collectionType?
Answer: Default to string.
- name: name-prefix # expects a string
- name: helm-parameters-incorrect # expects a string, the map is ignored
map:
global.image.repository: quay.io/argoproj/argocd
- name: helm-parameters # expects a map
collectionType: map
map:
global.image.repository: quay.io/argoproj/argocd
- Question: What do we do if a parameter has a missing or absent top-level
namefield?
Answer: Throw a validation error in the CMP server when handling an announcement. Throw a validation error in the controller and mark the Application as unhealthy if the invalid spec is in the Application. Throw an error in the CMP server and refuse to generate manifests in the CMP server if given invalid parameters.
# needs a `name` field
- title: Parameter Overrides
collectionType: map
map:
global.image.repository: quay.io/argoproj/argocd
Detailed examples¶
Example 1: trivial parameterized CMP¶
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ConfigManagementPlugin
metadata:
name: trivial-cmp
spec:
version: v1.0
generate:
command:
- sh
- -c
- |
# Pull one parameter value from the "main" section of the given parameters.
CM_NAME_SUFFIX=$(echo "$ARGOCD_APP_PARAMETERS" | jq -r '.["main"][] | select(.name == "cm-name-suffix").value')
cat << EOM
{
"kind": "ConfigMap",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "$ARGOCD_APP_NAME-$CM_NAME_SUFFIX",
"namespace": "$ARGOCD_APP_NAMESPACE"
}
}
EOM
discover:
fileName: "./trivial-cmp"
parameters:
command:
- sh
- -c
- |
echo '[{"name": "cm-name-suffix"}]'
Example 2: Helm parameters from Kustomize dependency¶
Plugin config
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ConfigManagementPlugin
metadata:
name: kustomize-helm-proxy-cmp
spec:
version: v1.0
generate:
command: [/home/argocd/generate.sh]
discover:
fileName: "./kustomization.yaml"
parameters:
static:
- name: version
title: VERSION
string: v4.3.0
- name: name-prefix
title: NAME PREFIX
- name: name-suffix
title: NAME SUFFIX
dynamic:
command: [/home/argocd/get-parameters.sh]
generate.sh
This script would be non-trivial. Kustomize only accepts YAML-formatted values for Helm charts. The script would have to convert the dot-notated parameters to a YAML file.
get-parameters.sh
kustomize build . --enable-helm > /dev/null
get_parameters() {
while read -r chart; do
yq e -o=p "charts/$chart/values.yaml" | jq --arg chart "$chart" --slurp --raw-input '
{
name: "\($chart)-helm-parameters",
title: "\($chart) Helm parameters",
tooltip: "Parameter overrides for the \($chart) Helm chart.",
collectionType: "map",
map: split("\\n") | map(capture("(?<key>.*) = (?<value>.*)")) | from_entries
}'
done << EOF
$(yq e '.helmCharts[].name' kustomization.yaml)
EOF
}
# Collect the parameters generated for each chart into one array.
get_parameters | jq --slurp
Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu:20.04
RUN apt install jq yq helm kustomize -y
ADD get-parameters.sh /home/argocd/get-parameters.sh
Example 3: simple Helm CMP¶
This example demonstrates how the Helm parameters interface could be achieved with a parameterized CMP.
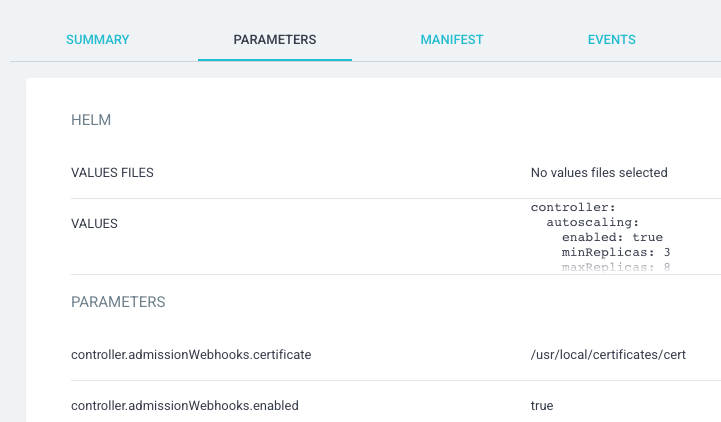
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ConfigManagementPlugin
metadata:
name: simple-helm-cmp
spec:
version: v1.0
generate:
command: [/home/argocd/generate.sh]
discover:
fileName: "./values.yaml"
parameters:
static:
- name: values-files
title: VALUES FILES
collectionType: array
dynamic:
command: [/home/argocd/get-parameters.sh]
generate.sh
# Convert the values-files parameter value to a newline-delimited list of Helm CLI arguments.
ARGUMENTS=$(echo "$ARGOCD_APP_PARAMETERS" | jq -r '.[] | select(.name == "values-files").array | .[] | "--values=" + .')
# Convert JSON parameters to comma-delimited k=v pairs.
PARAMETERS=$(echo "$ARGOCD_APP_PARAMETERS" | jq -r '.[] | select(.name == "helm-parameters").map | to_entries | map("\(.key)=\(.value)") | .[] | "--set=" + .')
# Add parameters to the arguments variable.
ARGUMENTS="$ARGUMENTS\n$PARAMETERS"
echo "$ARGUMENTS" | xargs helm template .
The manifest generation command will be
helm template . --values=a.yaml --values=b.yaml --set=image.repo=alpine --set=image.tag=latest
for the following value of $ARGOCD_APP_PARAMETERS:
[
{
"name": "values-files",
"array": ["a.yaml", "b.yaml"]
},
{
"name": "helm-parameters",
"map": {
"image.repo": "alpine",
"image.tag": "latest"
}
}
]
get-parameters.sh
yq e -o=p values.yaml | jq --slurp --raw-input '
[{
name: "helm-parameters",
title: "Helm Parameters",
collectionType: "map",
map: split("\\n") | map(capture("(?<key>.*) = (?<value>.*)")) | from_entries
}]'
Consider a very simple values.yaml:
image:
repo: quay.io/argoproj/argocd
tag: latest
The script above will produce the following parameters announcement:
[
{
"name": "helm-parameters",
"title": "Helm Parameters",
"collectionType": "map",
"map": {
"image.repo": "quay.io/argoproj/argocd",
"image.tag": "latest"
}
}
]
Example 4: simple Kustomize CMP¶
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ConfigManagementPlugin
metadata:
name: kustomize
spec:
parameters:
static:
- name: version
title: VERSION
string: v4.3.0
- name: name-prefix
title: NAME PREFIX
- name: name-suffix
title: NAME SUFFIX
dynamic:
command: ["generate-params.sh"]
parameters.dynamic.command will produce something like this:
[
{
"name": "images",
"title": "Image Overrides",
"collectionType": "map",
"map": {
"quay.io/argoproj/argocd": "docker.example.com/proxy/argoproj/argocd",
"ubuntu:latest": "docker.example.com/proxy/argoproj/argocd"
}
}
]
Security Considerations¶
Increased scripting¶
Our examples will have shell scripts, and users will write shell scripts. Scripts are difficult to write securely - this is especially true when the scripts are embedded in YAML, and developers don't get helpful warnings from the IDE.
Our docs should emphasize the importance of handling input carefully in any scripts (or other programs) which will be executed as part of CMPs.
The docs should also warn against embedding large scripts in YAML and recommend plugin authors instead build custom images with the script invoked as its own file. The docs should also recommend taking advantage of IDE plugins as well as image and source code scanning tools in CI/CD.
Risks and Mitigations¶
- Risk: encouraging CMP adoption while missing critical features from native tools.
Mitigation: rewrite the Helm config management tool as a CMP and test as many common use cases as possible. Write a document before starting on the Helm CMP documenting all major features which must be tested.
Upgrade / Downgrade Strategy¶
Upgrading will only require using a new version of Argo CD and adding the parameters settings to the plugin config.
Downgrading will only require using an older version of Argo CD. The parameters section of the plugin config will
simply be ignored.
Drawbacks¶
Sidecar CMPs aren't really battle-tested. If there are major issues we've missed, then moving more users towards CMPs could involve a lot of growing pains.